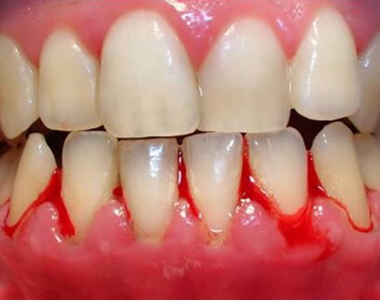
Stop Bleeding and Inflamed Gums with These Easy Solutions
Bleeding and inflamed gums, medically termed gingivitis, are common oral health problems often indicative of underlying periodontal disease. While a temporary instance of bleeding gums might stem from vigorous brushing, persistent bleeding and inflammation signal a need for immediate attention and proactive intervention. Untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a severe form of gum disease leading to tooth loss. This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, and effective strategies for managing and resolving bleeding and inflamed gums.
Understanding the Root Causes of Bleeding and Inflamed Gums
The primary culprit behind bleeding and inflamed gums is plaque, a sticky biofilm of bacteria that constantly forms on teeth. Poor oral hygiene practices allow plaque to accumulate, triggering an inflammatory response in the gums. This inflammation manifests as redness, swelling, and bleeding. Several factors contribute to the development and exacerbation of this condition:
Poor Oral Hygiene
Insufficient brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up along the gum line and between teeth, creating an ideal breeding ground for harmful bacteria. This bacterial colonization initiates the inflammatory process leading to gingivitis.
Genetics
Genetic predisposition plays a role in susceptibility to gum disease. Some individuals may inherently have a weaker immune response or gum tissue structure, making them more prone to inflammation and bleeding.
Hormonal Fluctuations
Hormonal changes, particularly during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can influence gum health. These fluctuations can increase susceptibility to inflammation and bleeding.
Systemic Diseases
Certain systemic diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and HIV/AIDS, can affect gum health and increase the risk of severe gum disease. These conditions can compromise the immune system, making individuals more vulnerable to infections.
Smoking
Smoking significantly impairs the body's ability to fight infections, making smokers much more likely to develop and experience severe gum disease. Smoking also restricts blood flow to the gums, hindering healing and increasing the risk of complications.
Medications
Certain medications, including some blood thinners and immunosuppressants, can increase bleeding tendencies, contributing to gum bleeding. Always inform your dentist about all medications you are taking.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Bleeding and Inflamed Gums
Early detection is crucial for effective management of gum disease. The initial symptoms are often subtle and might be easily overlooked. However, consistent monitoring and awareness of the following signs are essential:
- Bleeding gums: This is the most prominent symptom, often occurring during or after brushing and flossing.
- Red, swollen gums: Inflamed gums appear noticeably redder and more swollen than healthy gums.
- Tender, painful gums: Gums may be sensitive to touch or pressure.
- Receding gums: Over time, inflamed gums may recede, exposing more of the tooth root and increasing susceptibility to cavities and tooth loss.
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis): Bacterial buildup contributes to unpleasant breath odor.
- Loose teeth: In advanced stages, gum disease can cause teeth to loosen and eventually fall out.
Effective Strategies for Managing and Resolving Bleeding and Inflamed Gums
Addressing bleeding and inflamed gums requires a multi-faceted approach that combines proper oral hygiene, lifestyle modifications, and, in some cases, professional dental intervention.
Improved Oral Hygiene Practices
The foundation of gum health lies in meticulous oral hygiene. This includes:
- Brushing twice daily: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Brush gently in circular motions for at least two minutes each time.
- Flossing daily: Flossing removes plaque and food particles from between teeth where a toothbrush cannot reach.
- Using an antimicrobial mouthwash: An antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce bacterial load and further improve oral hygiene.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle choices significantly impact gum health. Consider the following changes:
- Quitting smoking: Smoking significantly increases the risk of gum disease. Quitting is crucial for improving gum health and overall well-being.
- Managing systemic diseases: Effectively managing conditions like diabetes can significantly reduce the risk of gum disease complications.
- Maintaining a balanced diet: A nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall health, including oral health.
- Reducing stress: Stress can negatively impact the immune system, increasing susceptibility to inflammation.
Professional Dental Care
Regular visits to the dentist are essential for maintaining optimal gum health. Professional cleaning removes plaque and tartar buildup that cannot be removed through home care. The dentist can also diagnose and treat any underlying gum disease.
Home Remedies and Additional Treatments
While professional care is crucial, some home remedies can complement the treatment plan and provide additional relief:
- Saltwater rinses: Rinsing with warm saltwater can help reduce inflammation and soothe irritated gums.
- Tea tree oil: Some studies suggest that tea tree oil possesses antibacterial properties that may help fight gum infections. However, it should be used cautiously and diluted properly.
- Aloe vera: Aloe vera gel has soothing and anti-inflammatory properties that can provide temporary relief from gum inflammation. It should be used topically with caution.
Disclaimer: This article provides general information and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a dentist or other qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition. The information provided here is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical guidance.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.